RISK MANAGEMENT
A well-defined risk management framework is integral to any business, but is especially important during times of uncertainty. The outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020, and its resurgence has prolonged macro-economic uncertainty. During such period, there is a greater focus on optimal capital deployment and risk- adjusted returns on capital. Well-governed companies must reinforce their risk management capabilities and not only satisfy regulatory requirements, but set themselves up for success post the period of uncertainty.

Enterprise Risk Management
PEL has an independent and dedicated Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) system to identify, manage and mitigate business risks. Risk management, internal controls and assurance processes are embedded into all activities of the Company.
PEL’s ERM framework is designed by integrating COSO* framework at its core
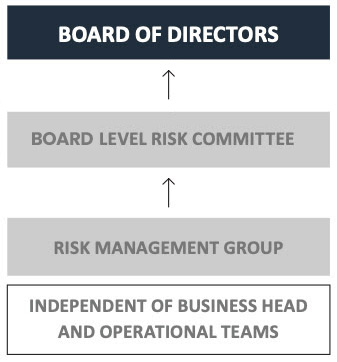
The Risk Management Group (RMG) establishes the risk policies and processes for risk evaluation and measurement; and business units focus on developing and implementing mitigation measures while taking controlled risks. Specific risk approaches are in place for both the Financial Services and Pharma businesses.
In Financial Services, as PEL is executing its transformation agenda, it becomes imperative to follow a systematic approach to identify, assess, prioritize and mitigate risks. In the Pharma business, the Company’s focus remains on business continuity and securing the supply chain, in order to deliver consistent performance and invest in growth opportunities.
The Company ensures seamless interaction between the Strategic Business Units (SBUs) and RMG to assess the real risks and their severity. The RMG is independent of SBUs and reports directly to the Board.
*COSO - Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission
The Board
The Board oversees PEL’s risk management programme. It regularly reviews and evaluates the programme to ensure that adequate policies, procedures and systems are in place to execute the strategy and manage related risks. The Board-level ‘Risk Committee’ reviews the micro-level risks and reports it to the Board. Additionally, the Risk Management Committee for Financial Services (FS) – formed in FY 2018 – focuses on strategy and risk management practices followed in the FS business unit.
The RMG periodically appraises the portfolio health in the FS vertical and the risk profile of the business verticals in non-financial services (non-FS) businesses to the Board.
Key milestones and initiatives – Risk Management Group
2014-15
- ERM Policy
- Risk Evaluation Model
- ALM Policy
- Risk Ratings
- Risk Register(non-FS)
2016-17
- Portfolio Analysis
- Transfer Pricing Mechanism (FS)
- Model Development (new FS product)
- Limits Framework
- Product-wise Provisioning (ECL)
- Corporate Governance Review
2018-19
- Annual Macroeconomic Stress Testing
- Credit Approval Authorization Matrix (CAAM)
2020-22
- Revising Frameworks for Sectoral Limits
- ALM Analysis
- COVID-19 stress testing (wholesale and retail portfolios)
- Retail Fraud Control Unit (FCU)
- New Risk Model Development
- Portfolio Risk Assessment (outlook)
- Risk Control Matrix
- Enterprise Risk Management
Financial Services
The RMG independently assesses all investments and loans of PEL’s FS business. The Group uses internal risk assessment models to evaluate credit, market and concentration risks embedded in any deal. Based on the assessment, the RMG recommends a plan to mitigate or to eliminate the identified risks in the investments. The enterprise-wide limits framework for lending and the corresponding delegation of authority based on such limits addressing the extent of exposures at transaction and portfolio-level take into consideration product idiosyncrasies as well. Also, similar matrices for delegation of authority corresponding to transaction-level approvals are used by the Company.
Retail Risk Management
The Company is transforming its Financial Services business from a ‘wholesale-led’ business model to a ‘well-diversified’ business. In November 2020, the Company launched its multi-product retail lending platform, while expanding its geographic presence and customer reach. As Retail Lending is an operations intensive, volume driven business with smaller ticket sizes, it requires a risk management architecture to control default and fraud risk at a micro-level. Technology and analytics have enabled new risk-management techniques, faster computing power to facilitate better risk decision support and process integration.
Retail Risk Management is a part of the Risk Management Group (RMG).
RMG performs the following broad-level functions for retail risk management.
- Risk reviews of the retail loans are conducted periodically to analyse traits of the portfolio
- Risk policies and the changes therein are reviewed periodically by RMG, and approved by the Board
- RMG approves frameworks and policies for engaging with Fintech partners for technology-intensive lending programs
In the retail segment, creditworthiness of a borrower is determined based on the policy and process standards set by the Company. There are several credit checks and controls at multiple stages of the loan process to ensure and strengthen the asset quality of the portfolio.
Operational Risk and Fraud Risk
Fraud risk management committee (‘FRMC’) comprising of top management representatives is constituted, which oversees the matters related to fraud risk, reviews and approves actions against frauds. FRMC reviews findings of various investigations, identified fraud prone areas and approves mitigation measures. Status of mitigation measures are reviewed periodically.
The Company’s Enterprise Risk Management framework considers Credit Risk, ALM Risk, Operational Risk, Fraud Risk as the key risk in addition to strategic and compliance risks etc.
The Company has an elaborate system of internal audit and concurrent audit commensurate with the size, scale and complexity of its operations and covers funding operations, financial reporting, fraud control and compliance with laws and regulations. Further, Concurrent audit helps prevent and address document related anomalies and deficiencies which strengthen quality assurance during onboarding and processing of transactions.
Internal Auditors monitors and evaluates the efficacy and adequacy of internal control systems in the Company, its compliance with laws and regulations, efficacy of its operating systems, adherence to the accounting procedures and policies at all offices of the Company and report directly to Audit and Risk Management Committee of the company.
Risk Management – Wholesale Lending
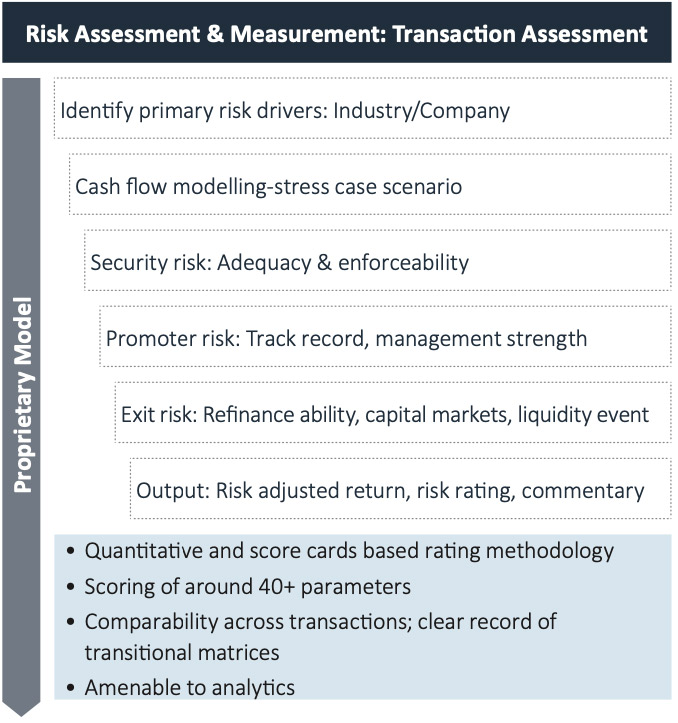
Risk Assessment Approach
The approach involves identification and measurement of risk for each investment. Risks are classified into quantifiable and non- quantifiable risks.
1) Quantifiable risks are estimated as the deficit in Cash Flow
2) Non-quantifiable risks are estimated through comprehensive scorecards and standard mark-ups
- Security value, promoter evaluation, exit options, etc. are rated through scorecards
- Operational and concentration risks are covered by applying standard mark-ups (multiples) to the risk-weights, for determining the risk rating of a deal
The Risk team considers various factors, such as historical performance, execution capability, financial strength of the promoter and company, competitive landscape in the industry and specific segment, regulatory framework and certainty, impact of macroeconomic ‘changes’, etc. while assessing the deal. The security structure is assessed for value, enforceability and liquidity. The rating generated is used for internal benchmarking and pricing. The Credit team takes inputs from the RMG to arrive at optimal deal structuring.
Framework to evaluate Risk Adjusted Returns
The Risk team assesses every loan proposal independently using proprietary risk assessment models.
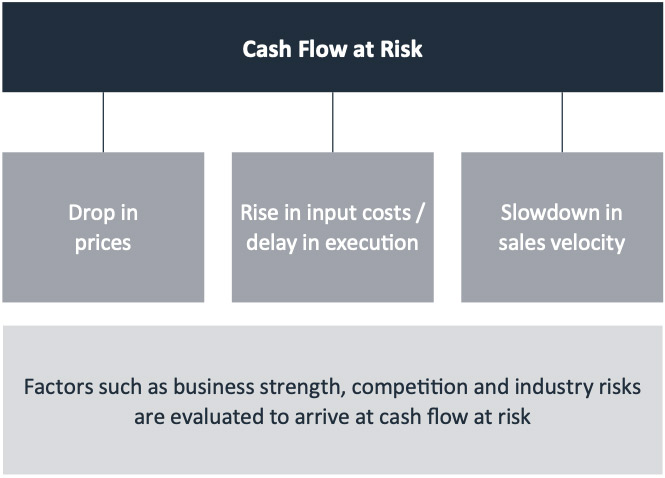
Appropriate Stress is Assumed for Key Project Variables to Compute Cash Flow at Risk
Portfolio Revaluation Process
All executed deals are re-valued by the RMG at regular intervals. The portfolio revaluation provides the Management with latest overview of the portfolio performance. It also triggers specific action plans for identified deals and data-based insights for enhancing the underwriting criteria for future deals.
Underwriting and Risk Mitigation
Generally, a conservative, data-driven underwriting and structuring approach is adopted. The deal related risks and the risks emanating from exogenous events are thoroughly analysed as part of the risk assessment process. The impact of any event on specific micro- markets, industries and product segments are carefully analysed and the deal underwriting criteria is altered accordingly.
Governance Structure:
A robust governance structure for the risk management process has been put in place. Various committees, both at the senior executive management level and at the Board sub-committee level, have been formed to evaluate risk and the risk management process at PEL.
Impact of COVID-19:
The outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic across the globe and in India has contributed to a significant decline and volatility in the global and Indian financial markets and slowdown in the economic activities.
The extent to which the COVID-19 pandemic, will continue to impact the Company’s performance will depend on ongoing as well as future developments, which are uncertain, including, among other things, any new information concerning the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic and any action to contain its spread or mitigate its impact whether government-mandated or elected by the Company. Given the uncertainty over the potential macro-economic conditions and other related matters, the impact of the global health pandemic may be different from the estimated as at the date of approval of these financial results and the Company will continue to closely monitor any material changes to the future economic conditions including impact on expected credit losses.
Pharma Business
We have an independent and dedicated Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) system to identify, manage and mitigate business risks. Risk management, internal controls and assurance processes are embedded into all our activities. The following are the activities of ERM:
- The Risk Management Group (RMG) establishes the risk policies and processes for risk evaluation and measurement
- Business units focus on developing and implementing mitigation measures while taking controlled risks
- Our Board oversees risk management programme and are the trustee to protect and enhance stakeholders’ value through supervision and strategic inputs
- Board members are responsible for developing the Company’s vision, strategic goals and policies, and monitors performance
- Board reviews and evaluates the programme to ensure that adequate policies, procedures and systems are in place to execute the strategy and manage risks
- The ‘Risk Committee’ reviews the micro-level risks and reports them to the Board
- Our business units focus on developing and implementing mitigation measures whilst taking controlled risks. Specific risk approaches are designed for businesses
Risk assessment at Pharma business units is carried out using risk registers. Risks across different business units, their probability, impact and mitigation plans are properly documented at regular intervals. These risks are then aggregated, and key risks across each business unit, along with the proposed mitigants, are presented and reviewed by the Board on a periodic basis.
Another important focus area for PEL in mitigating risks associated with the non-Financial Services businesses is to harness quality as a culture. The Company strongly believes that quality is driven by concern for patient safety. An exemplary quality framework is implemented at PEL’s facilities as well as at several contract manufacturing operations. A deep commitment to building a quality- driven organisational culture has helped PEL achieve the highest level of regulatory compliance.
The two key risks faced by the Pharma industry due to COVID-19 were:
Business Continuity: As life-saving drugs are considered ‘essential’ by governments across the world, companies were required to make efforts to sustain operations and ensure that manufacturing facilities were operational during the lockdown periods.
Securing the supply chain: During a pandemic, supply chains can be at significant risk due to over-reliance on a location. As a result, companies may be required to reduce supplier concentration and reduce dependence on certain markets for raw materials. Some businesses may also be required to ramp-up production and inventory management to meet the higher demand for certain products amidst the pandemic (e.g. hand sanitizers, multi-vitamins and painkillers).
Major Risks and Mitigating Actions
The major risks perceived by PEL, along with the measures taken to mitigate them, are as follows:
| RISK | IMPACT | MITIGATING MEASURES |
| Default and concentration risk in the Financial Services business |
In the Financial Services (FS) business, the risk of default and non-payment by borrowers may adversely affect profitability and asset quality. The Company may also be exposed to concentration risks across sectors, counterparties and geographies. |
At PEL, each investment is assessed by the investment team as well as an independent risk team on the risk-return framework. The combined analysis of these teams is presented to the Investment Committee for investment decision. The large part of our loan book is secured in nature, with healthy security cover obtained at the time of deal origination. Moreover, the deals are based on conservative underwriting parameters. Concentration risk is partly mitigated by the concentration risk framework, which incentivises businesses to diversify portfolio across counterparties, sectors and geographies. Some of the key measures we continued during the year to mitigate default and concentration risks in the FS business are:
In Q4 FY 2022, the Company re-evaluated its wholesale portfolio to detect any lasting impacts on its clients of the pandemic or recent stresses in the macro-economy. Based on this assessment, some non-real estate exposures were moved to Stage 2 and thus, the Company has made additional provisioning and interest reversal of ₹ 1,037 Crores for the same. This includes additional provisioning of ₹ 822 Crores and interest reversal of ₹ 215 Crores against loans of ₹ 2,292 Crores. These were high-yield, structured mezzanine loans done under the 'Holdco' structure. The Company has discontinued doing such kind of deals. Hence total provisions increased to ₹ 3,735 Crores (5.7% of our AUM) as of March 2022, however, GNPA and NNPA ratios remain broadly unchanged qoq as of March 2022. |
| Client and product concentration risk in the Pharma business |
Client Concentration: Pharma business has some major contracts with few customers. Any set back at customers’ end may adversely affect the Company’s financials. Product Concentration: Decrease in sale of products with a significant share in revenue may lead to adverse profit margins. |
PEL’s business development teams continue to actively seek to diversify its client base and products to mitigate concentration risk. The Pharma business continues to focus on backward integration, alternative vendor development and geographically-diverse production facilities, to ensure production is closer to end markets. The Company also acquired niche products to reduce its dependence on inhalation anaesthesia in the Global Pharma Products business. |
| Product and quality risk |
PEL is expected to maintain global quality standards in manufacturing as some of the products are directly consumed/applied by consumers. Any deviation with regard to quality compliance of products would impact consumers worldwide, and hence, adversely affect the Company’s performance. |
A dedicated Corporate Quality Assurance Group actively monitors adherence to prescribed quality standards. PEL has a strong governance and escalation mechanism. The Company’s quality management system is independent of its businesses and reports directly to the Board. PEL is on a quality advancement journey from 'Quality for Compliance' to 'Quality as a Culture', with a focus on systems, processes, technology and people. PEL has successfully cleared 36 USFDA inspections, 269 total regulatory inspections, and 1,377 customer audits since the beginning of FY 2012. |
| Adverse fluctuations in foreign exchange risk |
PEL has significant revenues in foreign currencies through exports and foreign operations. Thus, the Company is exposed to risks arising out of changes in foreign exchange rates. |
The centralised treasury function aggregates the foreign exchange exposures and takes prudent measures to hedge these exposures based on prevalent macro-economic conditions and in line with applicable regulatory guidelines. |
| Interest rate risk |
Volatility in interest rates on investments, loans and treasury operations could cause the net interest income to decline adversely, affecting profitability of the Financial Services business. |
ALCO (Asset Liability Committee) actively reviews the interest rate risk and ensures that interest rate gaps are maintained as per ALCO’s interest rate view. With 79% of borrowings as ‘fixed rate liabilities’ and 63% of assets at floating rate, as of March 2022, the Financial Services business is well positioned to navigate the rising interest rate environment. |
| Liquidity and ALM risk |
Mismatch in the tenor of assets and liabilities in the Financial Services business could lead to liquidity risk. |
ALCO reviews the GAP statements and formulates appropriate strategy to manage the risk. In the last two years, the Company has shifted its borrowing mix towards long-term funding sources and reduced its exposure to Commercial Papers. During FY 2022, the Company raised ~` 19,550 Crores via 10-year NCDs to fund the DHFL acquisition. As a result, the ALM profile has significantly improved, with positive ALM GAP between cumulative inflows and cumulative outflows across all maturity buckets as on March 31, 2022. The Financial Services business had cash & cash equivalents of ` 8,533 Crores, as of March 31, 2022. |
| Financial Leverage |
The Company needs to be adequately capitalized both at the Group-level and in Financial Services. This serves as a buffer to absorb any risks arising from a volatile market/business environment and helps the Company to meet regulatory requirements from RBI/ NHB. |
Since the beginning of FY 2020, the Company has raised more than ` 18,000 Crores of equity capital and significantly deleveraged the balance sheet. As a result, the net debt-to-equity reduced to 1.2 times as of March 2022 compared to 2.0 times as of March 2019. Financial Services had an equity base of ` 17,006 Crores as of March 2022 and the net debt-to-equity for the Financial Services business stood at 2.7 times as of March 2022 versus 3.9 times as of March 2019. |
| Regulatory risk |
PEL requires certain statutory and regulatory approvals for conducting businesses. Any failure to obtain, retain or renew them in a timely manner may adversely affect operations. A change in laws or regulations made by the government or a regulatory body can increase the costs of operating a business, reduce the attractiveness of investment and/or change the competitive landscape. Also, PEL is structured through various subsidiaries across various countries in a tax-efficient manner. Regulatory changes in terms of repatriation and funding may lead to adverse financial impacts. |
The applicable regulatory framework is continuously tracked by various teams within PEL. Necessary and appropriate actions are undertaken to ensure compliance with all regulatory requirements. |
| Investment risk |
PEL has equity investments in various companies in India which are exposed to systematic and unsystematic risks. |
The Company continues to effectively evaluate various risks involved in underlying assets, before and after making any such strategic investments. These investments are re-valued and appropriate valuation adjustments are taken into consideration. |
| Environment |
PEL is committed to conserving resources as it recognises the importance of preserving the environment. Any non-adherence to the Company’s approved EHS practices and procedures may expose it to adverse consequences. |
The Company has adopted the 'reduce, reuse and recycle' mantra for natural resources. Several sustainability initiatives are underway in areas such as reduction of carbon footprint, water conservation, waste re-use / re-cycle. The Company has recently embarked upon a sustainability journey and an external consultant is helping it on the same. These efforts have helped the Company to significantly improve its Bloomberg ESG score and it was ranked 12th in the BW Businessworld India’s Most Sustainable Companies. |
| Client and product concentration risk in the Pharma business |
Client Concentration: Pharma business has some major contracts with few customers. Any set back at customers’ end may adversely affect the Company’s financials. Product Concentration: Decrease in sale of products with a significant share in revenue may lead to adverse profit margins. |
Our business development teams continue to actively seek to diversify our client base and products to mitigate concentration risk. We continued to focus on backward integration, alternative vendor development and geographically-diverse production facilities, to ensure production is closer to end markets. We also acquired niche products to reduce our dependence on inhalation anaesthesia in the global pharma products business. |
| Technology Risk |
Persons having permitted or illegal access to our information technology systems or infrastructure might do serious damage to our business and activities. This might cause legal claims, regulatory fines or reputational harm. |
We use secure computers and servers, have the latest version of the software, and use data back-ups that include off-site or remote storage. We also use anti-virus, anti-spyware protection, and firewalls. We have a robust cyber security framework in place. |
| Supply interruptions |
Our business is reliant on our manufacturing facilities. Any manufacturing facility shutdowns or other manufacturing or production challenges caused by unanticipated circumstances may result in lower sales and have a negative impact on our company. |
We have multiple manufacturing facilities spread across different countries. So even if one of them temporarily shuts down, we can fulfil the customer requirement through the other facility. In terms of the supply chain, we are not reliant on a few suppliers. We have multiple suppliers to fulfil our requirements. Our teams have been working on a project to broaden our vendor base and secure alternative suppliers attempting to mitigate supplier concentration and location risks in the event of an unexpected contingency in the future. |
| Licensing Requirements |
We must acquire and maintain licences, permits, product registrations, and other regulatory approvals from a variety of governmental authorities, as well as adhere to their operating and security requirements. Any failure may have a negative impact on the company. |
We continuously track the requirements imposed by the licensing authorities or other authorities and necessary steps are taken to adhere to those requirements. |
| Difficulty in merging firms |
We may not be able to achieve the forecasted additional revenue post acquiring a company. We may incur significant extra debt and contingent liabilities, or our continuing operations may be disrupted. |
Mergers and acquisitions are well-considered moves. We choose only those companies whose capabilities are complementary to us, who are synergistic to our company. We have had a lot of acquisitions, thus we are fairly experienced in making the right decision. Our global team is diversified across many cultures. We also put in conscious effort to align the culture and value system of the acquired business with ours. During FY 2022, we successfully integrated and re-activated DHFL’s branches, rolled-out management hierarchies for the employees absorbed by the Company and harmonized grades and policies. |
| Demand |
Pharma products have a specified shelf life. If the demand forecast is overestimated, it can result in leftover inventory. Also, demand is easily affected by external factors. For example, during the peak of COVID-19, there was a decline in elective surgeries and our Complex Hospital Generics business experienced a major impact. |
We try to prepare most accurate forecast possible. To do so, we use various methods such as Artificial Intelligence, Pilot Studies, Regression Analysis, Sensitivity Analysis, Forecasting Models etc. |
Note: For Financial Services, PEL has a group-level risk management framework in place along with independent entity-level risk management frameworks for PCHFL and PHL Fininvest.